Global Hemp Fiber Market to Surpass $30 billion
A new analysis of the global hemp fiber market utilizing recent data suggests that the hemp fiber space will balloon to over $30 billion by 2033.
What is Hemp?
Hemp is a “bast” fiber, which means that the fiber-producing part of the plant is made up of strands that run its length. These strands surround the woody core of the stem. It grows quickly, is naturally resistant to many insect species, and needs little water to cultivate. It also has a deep root system, which helps to reduce soil loss and erosion. Additionally, it is useful in many different crop rotations.
Hemp production and processing can involve relatively large quantities of fertilizer and machinery. Both of these use a lot of water. Hemp is bulky. Therefore, transportation to processing centers can be costly and energy-intensive. Barriers to the wider adoption of hemp also exist. Though hemp has no psychoactive properties, it’s been demonized for belonging to the cannabis family.
Hemp Market Boom
Based on global hemp data from 2021-2024, the report anticipates the convergence of several key factors to spur the market, including growing “industrial demand for sustainable composites” and technological breakthroughs in hemp processing. Specifically, the authors highlight growing interest from the automotive and construction sectors for “lightweight, bio-based composite materials” and an abundance of funding for the research and development of new hemp fiber processing techniques as driving factors for the ballooning industry.
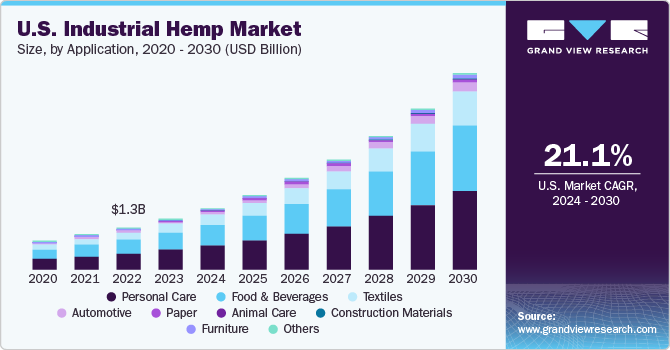
The report highlights significant hemp fiber market expansions across North America, Europe, and Asia, and notes that as of 2024, more than 60 countries have started hemp fiber production. The global hemp market saw approximately 200,000 tons of fiber production in 2021, the report said.
Technological Improvements in Hemp Industry
From Seed to Shelf: How Tech is Transforming Hemp
Hemp’s potential stretches far beyond its association with its cousin, cannabis. From building materials to clothing, food, and even beauty products, hemp is a game-changer. Let’s explore how technology is transforming hemp cultivation, processing, and product development:
- Precision Agriculture: Advanced sensors and data analytics are allowing hemp farmers to optimize growing conditions. New software monitors soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels, all to ensure the highest quality hemp yields.
- Gene Editing and Plant Breeding: Scientists are unlocking hemp’s full potential through genetic engineering. This allows for the development of hemp strains with specific characteristics, such as higher CBD content or improved fiber strength.
- Sustainable Processing Techniques: New extraction methods, like supercritical CO2 extraction, are revolutionizing how we extract valuable compounds from hemp. These techniques are not only efficient but also environmentally friendly – minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization.
- Nanotechnology Takes Root: The manipulation of matter at the atomic and molecular level is finding its way into the hemp industry. Hemp fibers are infused with nanoparticles to create stronger, lighter, and more durable materials for construction or textiles.
What does the future hold?
While the U.S. hemp market experienced “significant transformations” in 2024, including significant production increases despite “dramatic price corrections” for hemp fiber crops, China remains the world’s largest hemp fiber producer with an output of 73,000 metric tons in 2024, which is expected to surge to 117,000 metric tons in 2025.
Meanwhile, in Europe, France maintained its position as the continental powerhouse. The Netherlands has also emerged as a “rapidly growing player in the European hemp fiber market” with a year-over-year growth in hemp production of nearly 74% from 2023 to 2024.
In the United States, South Dakota leads the nation in hemp processing and the production of hemp fiber. There were 13.6 million pounds of hemp harvested for fiber in South Dakota last year.


