Cannabis Nutrient Disorders

Cannabis Nutrient Disorders
When troubleshooting nutrient disorders in cannabis, often the symptoms and possible culprits can be confusing. Additionally, the margins for success and failure can often be very small, making even incremental changes in cultural practices detrimental. Thus, learning the art and science of diagnostics is important and valuable.
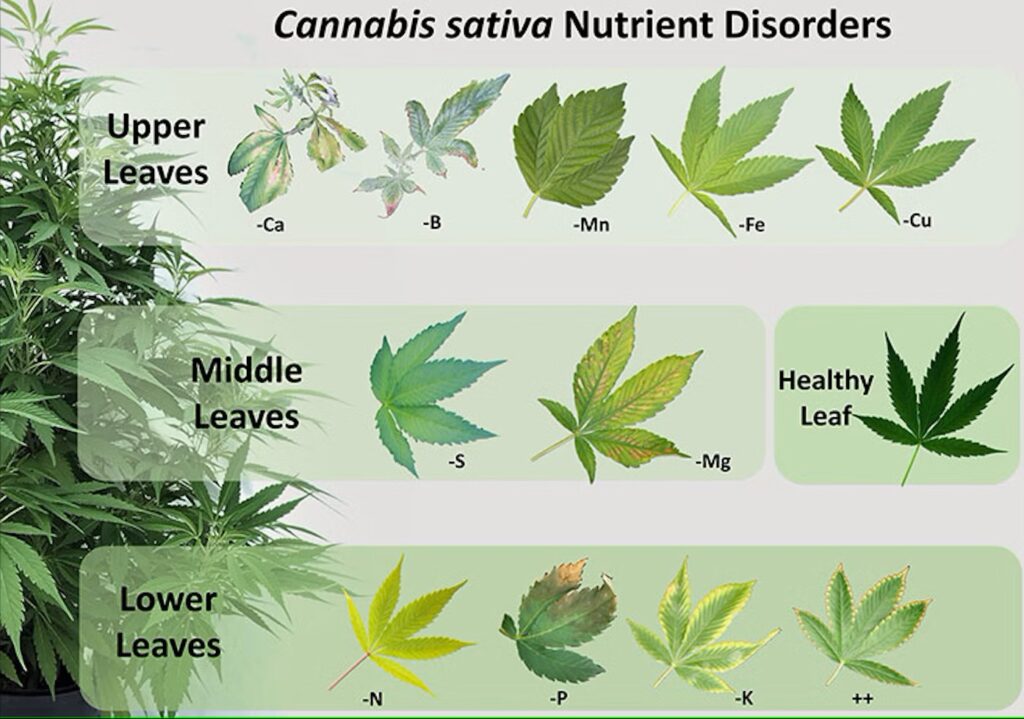
Deficiency Symptoms by Appearance
Group 1: Distorted growth and necrosis (Calcium and Boron)
Group 2: Overall yellowing (Nitrogen and Sulfur)
Group 3: Interveinal chlorosis (yellowing of tissue between veins) (Phosphorous and Iron)
Group 4: Marginal chlorosis and necrosis (death) (Potassium, Magnesium, Manganese, Zinc, and Molybdenum)
Causes and Solutions
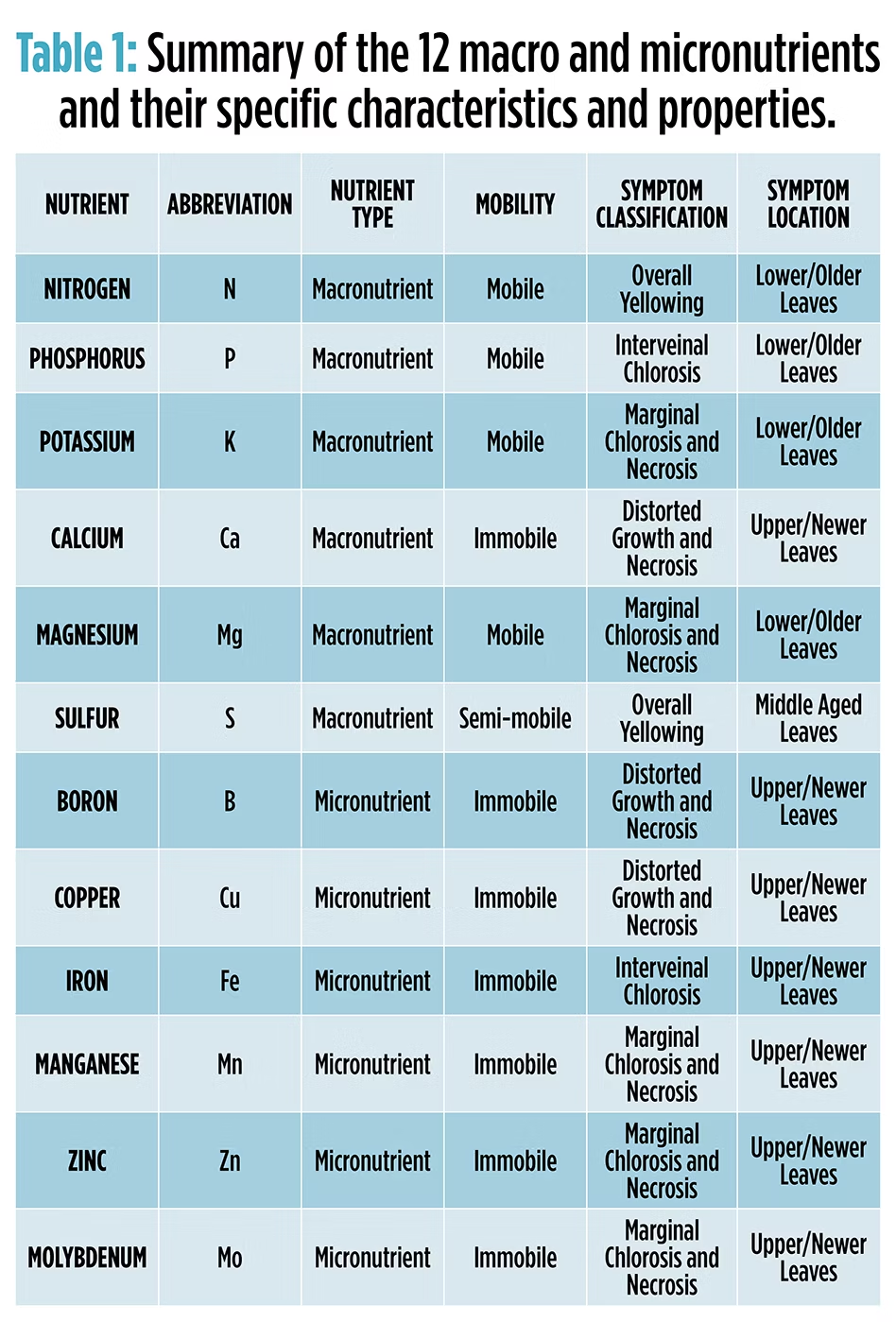
Cannabis plants require balanced nutrients for healthy growth. When nutrients are deficient or excessive, disorders occur. These issues affect plant health and yield significantly.
First, nitrogen deficiency is common in cannabis cultivation. It causes yellowing leaves and stunted growth. Cultivators often notice older leaves turning pale first. To correct this, apply a nitrogen-rich fertilizer promptly.
Finally, regular observation helps detect problems early. Check leaves, stems, and overall plant vigor daily. Use nutrient charts and testing kits for accurate diagnosis. Quick action prevents long-term damage and ensures healthy harvests.
Nutrient disorders in cannabis are manageable with knowledge and care. Balanced feeding, pH control, and monitoring are key strategies. Healthy plants reward growers with abundant, high-quality yields.